test tibial torsion site physio-pedia.com|test for tibial torsion : China Tibial Torsion - Etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, signs, diagnosis & prognosis from the Merck Manuals - Medical Professional Version.
WEB1/ El tipo de cambio (FIX) es determinado por el Banco de México con base en un promedio de cotizaciones del mercado de cambios al mayoreo para operaciones .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Early Access. $5. / month. Get Early Access to two new comic pages a week! 4 Weeks before they go public! *** Please note: You are charged immediately when pledging. All .
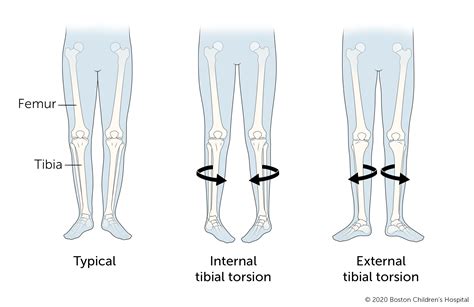
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .Thigh-foot angle (TFA): a means to measure tibial torsion. To measure internal or external tibial torsion, the patient is positioned in prone lying with their knees flexed to 90° and foot resting in its natural position. The TFA is measured .Tibial torsion causes the feet to turn inward, or have what is also known as a “pigeon-toed” appearance. The ability to compensate for tibial torsion depends on the amount of inversion .Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test (TPAT)'. [1]
External Tibial Torsion is a rare developmental condition in young children caused by abnormal external rotation of the tibia leading to an out-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle measuring .Tibial Torsion - Etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, signs, diagnosis & prognosis from the Merck Manuals - Medical Professional Version. Tibial torsion can be assessed by comparing the bimalleolar axis with the position of the tibial tubercle. Note the foot shape: Metatarsus adductus may be the primary cause of in-toeing, particularly in the infant.Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn .
Persistent, excessive torsion can lead to toeing-in and bowlegs. To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child .
Tibial torsion can be assessed by comparing the bimalleolar axis with the position of the tibial tubercle. Note the foot shape: Metatarsus adductus may be the primary cause of in-toeing, particularly in the infant.Standard radiographs of the knee can show several findings suggestive of acute PLC injury, including abnormal widening of the lateral joint space, fibular tip avulsion fracture or fracture of the fibular head, avulsion fracture off Gerdy’s .Original Editor - Lucinda hampton. Function [edit | edit source] Motor [edit | edit source]. At the popliteal fossa, branches of the tibial nerve supply medial and lateral heads of gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris and popliteus muscles. The popliteus branch goes on to supply tibialis posterior muscle, superior and inferior tibiofibular joint, tibiaand the interosseous membrane of leg.Valgus knee, or "knock knee", is a deformity of the lower leg where the knee joint angles outward from the body's midline.This condition is defined by a valgus angle of 10° or more.This deformity results from anatomical variations, including bone tissue remodeling and soft tissue contraction or elongation.. Bone tissue remodeling [edit | edit source]
sebbag schirmer tear test repeat
The menisci are fibrocartilaginous structures that function to deepen the tibial plateau, improve articulation of the femur on the tibia, stabilize the knee, and assist with shock absorption. The medial meniscus specifically forms almost a semicircular shape and covers 50-60% of the articular surface between the medial femoral condyle and the .
Description [edit | edit source]. Blount's disease, also known as infantile tibia vara, is a developmental growth disorder of the tibia that causes the lower leg to angle outwards, causing bowing of the leg. It is characterised by progressive multiplanar deformities of the leg caused by disordered endochondral ossification of the proximal medial tibial physis.Femoral anteversion or medial torsion of the femur is a condition that changes the alignment of the bones at the knee. This may lead to overuse injuries of the knee due to malalignment of the femur to the patella and tibia. The Q-angle: or quadriceps angle is the geometric relationship between the pelvis, the tibia, the patella and the femur and is defined as the angle between .The medial collateral ligament is a big ligament on the medial side of the knee. For more clinically relevant anatomy of the knee click here.The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is one of the four ligaments that are critical to maintaining the mechanical stability of the knee joint. The ligamentous sleeve spans the entire medial side of the knee from the medial aspect of the .Introduction [edit | edit source]. Lateral ligament injuries are perhaps one of the most common sports-related injuries seen by physiotherapists. Lateral ankle sprains are thought to be suffered by men and women at approximately the same rates; however, it is suggested that female interscholastic and intercollegiate basketball players have a 25% greater risk of incurring .
Clinically Relevant Anatomy [edit | edit source]. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone. It is located within the complex of the quadriceps and patellar tendon. Through its articulation with the femoral trochlea, the patellofemoral joint forms a highly complex unit with potential for joint instability. Patellofemoral joint stability is multifactorial and can be categorized into static and .
The ACL is a band of dense connective tissue which courses from the femur to the tibia.It is considered as a key structure in the knee joint, as it resists anterior tibial translation and rotational loads. The ACL arises from the posteromedial corner of the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle in the intercondylar notch and inserted anterior to the intercondyloid eminence of the .Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Navicular Drop Test (NDT) was first described by Brody in 1982 as a means of quantifying the amount of foot pronation in runners. It is the one of the static foot assessment tool and is intended to represent the sagittal plane displacement of the navicular tuberosity from a neutral position i.e. Subtalar joint neutral to a relaxed position in standing . Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) now known as Iliotibial Band Pain or lateral knee pain is a common knee condition that usually presents with pain and/or tenderness on palpation of the lateral aspect of the knee, superior to the joint line and inferior to the lateral femoral epicondyle.. It is considered a non-traumatic overuse injury, often seen in runners, and is often .
Achilles tendinopathy (common overuse injury) refers to a combination of pathological changes affecting the Achilles tendon usually due to overuse and excessive chronic stress upon the tendon. It can be seen both in athletes and non-athletes. It may or may not be associated with an Achilles tendon tear.A lack of flexibility or a stiff Achilles tendon can increase the risk of these .Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) insufficiency is the most common cause of adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. Failure of the tendon affects surrounding ligamentous structures and will eventually lead to bony .
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a heterogeneous non-progressive neuromotor disorder that affects movement and posture.[1] Primary impairments associated with cerebral palsy include spasticity, weakness, decreased motor control and movement dysfunction.[2] Cerebral palsy can also lead to a number of secondary musculoskeletal conditions, which can also .Transferring of the tibial tubercle (where the patellar tendon attaches to the tibia). The bony attachment of the tendon is moved more medially to allow the patella to track normally Used in conjunction with the lateral release and/or the medial .
Introduction [edit | edit source]. An ankle sprain is a common musculoskeletal injury that involves the stretch or tear (partial or complete) of the ligaments of the ankle joint. These injuries occur when the ankle moves outside of its normal range of motion which can be seen mostly in active and sports populations.Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .Bone Stress Injuries (BSI) are overuse injuries associated with repeated loading of bone by strenuous weight-bearing activities (such as running, jogging, marching) and inadequate recovery periods.BSI’s represent the failure of the skeleton bone to withstand repetitive loading, leading to structural fatigue, localized bone pain, and tenderness around the area.
Introduction [edit | edit source]. Sciatica refers to radiating pain along the course of the sciatic nerve from the lower back or buttock to one or both legs or an associated lumbosacral nerve root.. A common mistake is referring to any low back pain or radicular leg pain as sciatica.. Sciatica is a clinical diagnosis based on the presence of radiating pain in one leg, with or without the .Test: [edit | edit source] The patient is placed in side-lying and with the bottom leg bent. A pillow is placed between the therapist and the patient. During the modified test, the leg being tested is extended. The therapist will extend and abduct the hip. A negative test will consist of the patient being able to get 10° below parallel to the .Internal tibial torsion. Tibial torsion will typically re-model more quickly. We would expect the tibia to change from internal torsion at birth to approximately 10° of external torsion by the age of four to six years. Internal tibial torsion is beneficial in athletes, and becomes less symptomatic as femoral remodelling continues.
2. A positive drawer test done 5 days after the injury, has been shown to be more sensitive and specific than the test done withing the 24-48 hours. 3. A sensitivity of 52% has been reported in a single study for the inversion talar tilt test. 4. In acute injuries, the eversion stress test may be of limited clinical value.In some more complex cases, fractures can be managed by external fixation followed by further ORIF at a later time. Post tibial plateau fracture osteoarthritis is common (approximately one-third of all tibial plateau fractures) due to the articular surface being involved, despite the age of the patient at the time of fracture.. Physical Therapy Management [edit | edit source]
Anatomy of the Meniscus [edit | edit source]. The meniscus is C-shaped cartilage that acts as a cushion between the proximal tibia and the distal femur to make up the knee joint. It has an average width of 10 mm to 12 mm, and the average thickness is 4 mm to 5 mm. The meniscus is made of fibro-elastic cartilage. It is an interlacing network of collagen, proteoglycan, .Plantar fasciitis (Currently better referred to as Plantar Heel Pain) is the result of collagen degeneration of the plantar fascia at the origin, the calcaneal tuberosity of the heel as well as the surrounding perifascial structures. It is also called Plantar Fasciopathy (reflecting the absence of inflammation). The plantar fascia plays an important role in the normal biomechanics of the foot.
selected tear film tests in healthy cats
tibial torsion treatment pediatrics
My Friend Peppa Pig: Complete Edition - Sony .Playstation 5 & Playstation 4 [Digital Download]
test tibial torsion site physio-pedia.com|test for tibial torsion